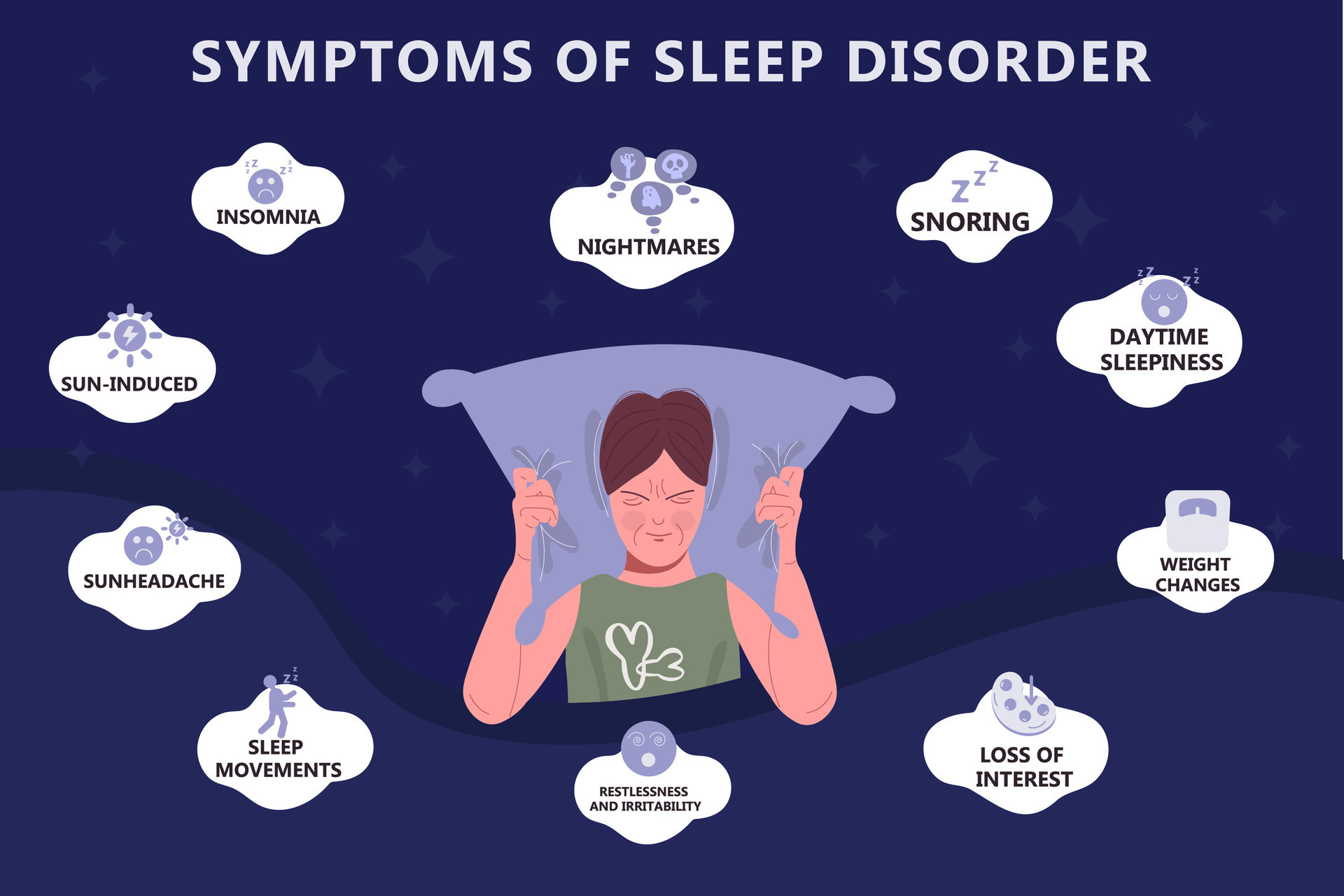
Medications such as Artvigil and Modalert 200 are frequently prescribed to treat sleep disorders, including obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and shift work sleep disorder. These substances are categorized as eugeroics, or wakefulness-promoting pharmaceuticals, an alternative term for therapies that enhance consciousness.
Armodafinil is present in Artvigil, whereas modafinil is the active constituent in Modalert 200. Both armodafinil and modafinil function by modulating dopamine levels in the brain, which are essential for regulating wakefulness and alertness.
In terms of modes of action and effects, Artvigil and Modalert 200 are remarkably similar. Nonetheless, the following distinctions exist:
Armodafinil is the active ingredient in Artvigil 150 mg, whereas modafinil is the active ingredient in Modalert 200. Since armodafinil is the R-enantiomer of modafinil, it possesses a greater concentration. Certain individuals argue that armodafinil exhibits a more gradual and sustained impact in comparison to modafinil.
In contrast to Artvigil, which is frequently offered in 150 mg capsules, Modalert 200 is only ever available in 200 mg tablets. Dosage recommendations may vary depending on the severity of the sleep disorder being treated and the patient’s individual requirements.
The half-life of armodafinil (Artvigil) is significantly longer than that of modafinil (Modalert), indicating that the former remains in the body for an extended period of time. This may lead to an extended duration of action and a reduction in the frequency of daily dosing.
Initially, Modalert 200 may exert its effects more rapidly than Artvigil, although the disparity is rarely perceptible
While these drugs are generally well tolerated, they, like all others, may cause adverse effects. Frequent adverse effects include insomnia, headache, nausea, and vertigo. Although infrequent, more severe adverse effects may manifest as chest pain, allergic reactions, and mood swings.
Certain pharmaceuticals may have drug interactions and may not be appropriate for all individuals; therefore, they must be taken under the guidance of a physician. Moreover, their efficacy is limited to symptom management rather than cure-all; thus, supplementary lifestyle modifications and therapeutic interventions may be advised as components of a comprehensive treatment regimen.